Business Loans for Service Expansion: How to Finance New Service Packages and Grow Your Business Exp...

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.

Business Loans for Service Expansion: How to Finance New Service Packages and Grow Your Business Exp...

Inventory Line of Credit: A Smart Strategy for Gradual Inventory Restocking Managing inventory is on...
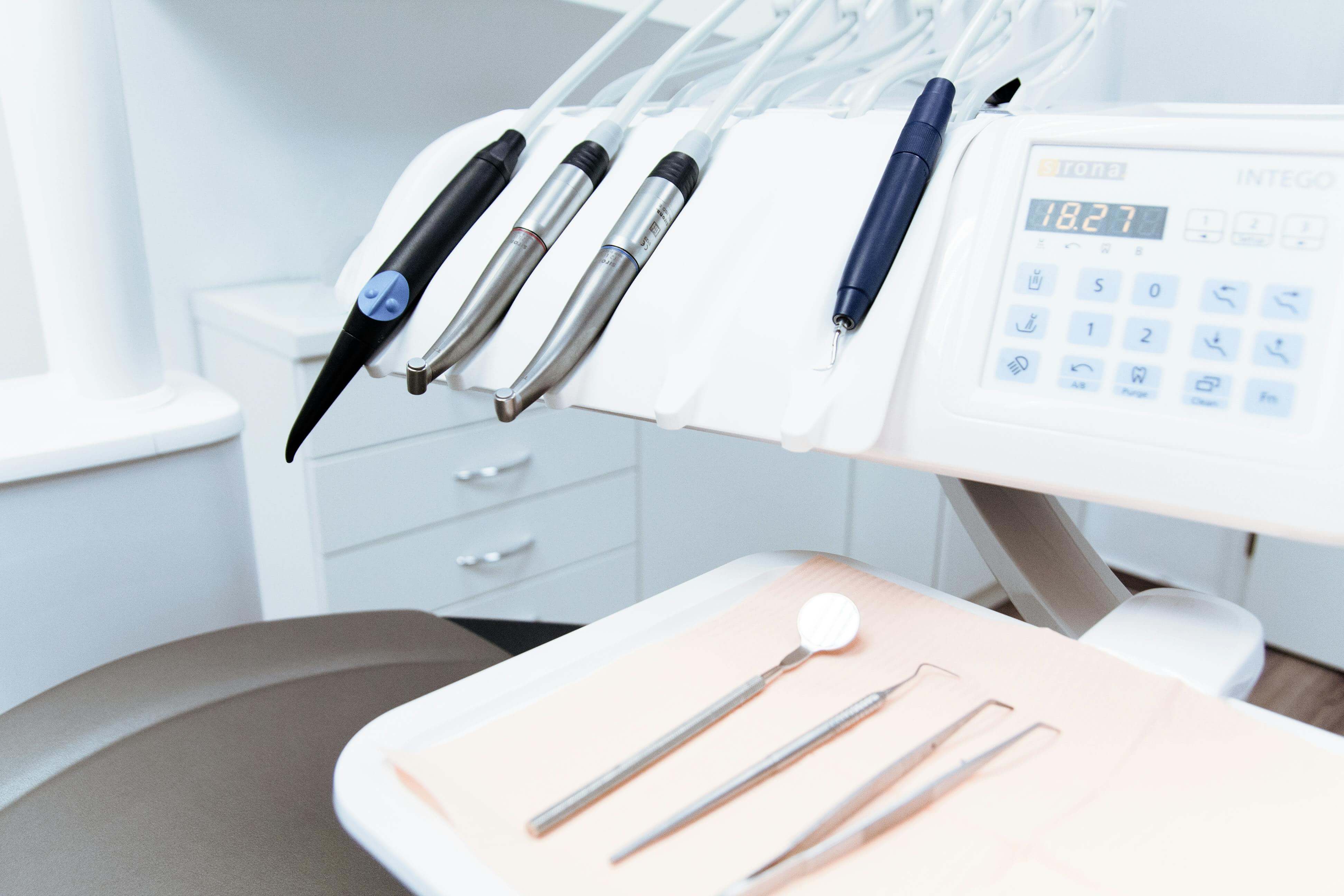
Equipment Financing for Reducing Human Error Human error remains one of the most expensive and persi...

Warehouse Expansion Financing: How to Expand a Warehouse Without Pausing Operations Expanding a ware...

Using a Business Line of Credit to Cover Deposits and Prepayments Many businesses face a common chal...

Loans for Creating a More Modern Client Environment First impressions matter more than ever in today...

Equipment Loans for Adding a Dedicated Testing Area Businesses across industries are investing in in...

Business Line of Credit for Seasonal Expenses: How to Handle Cost Spikes Without Hurting Cash Flow S...

Working Capital Loans for Managing Rapid Growth Cycles Rapid growth is every business owner's goal—b...

Equipment Financing for High-Volume Delivery Days High-volume delivery days can make or break logist...

Customer Experience Loans: How Businesses Finance Better Customer Experiences Customer expectations ...

Using a Business Line of Credit to Ease Cash Flow Between Contracts Many businesses experience uneve...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.