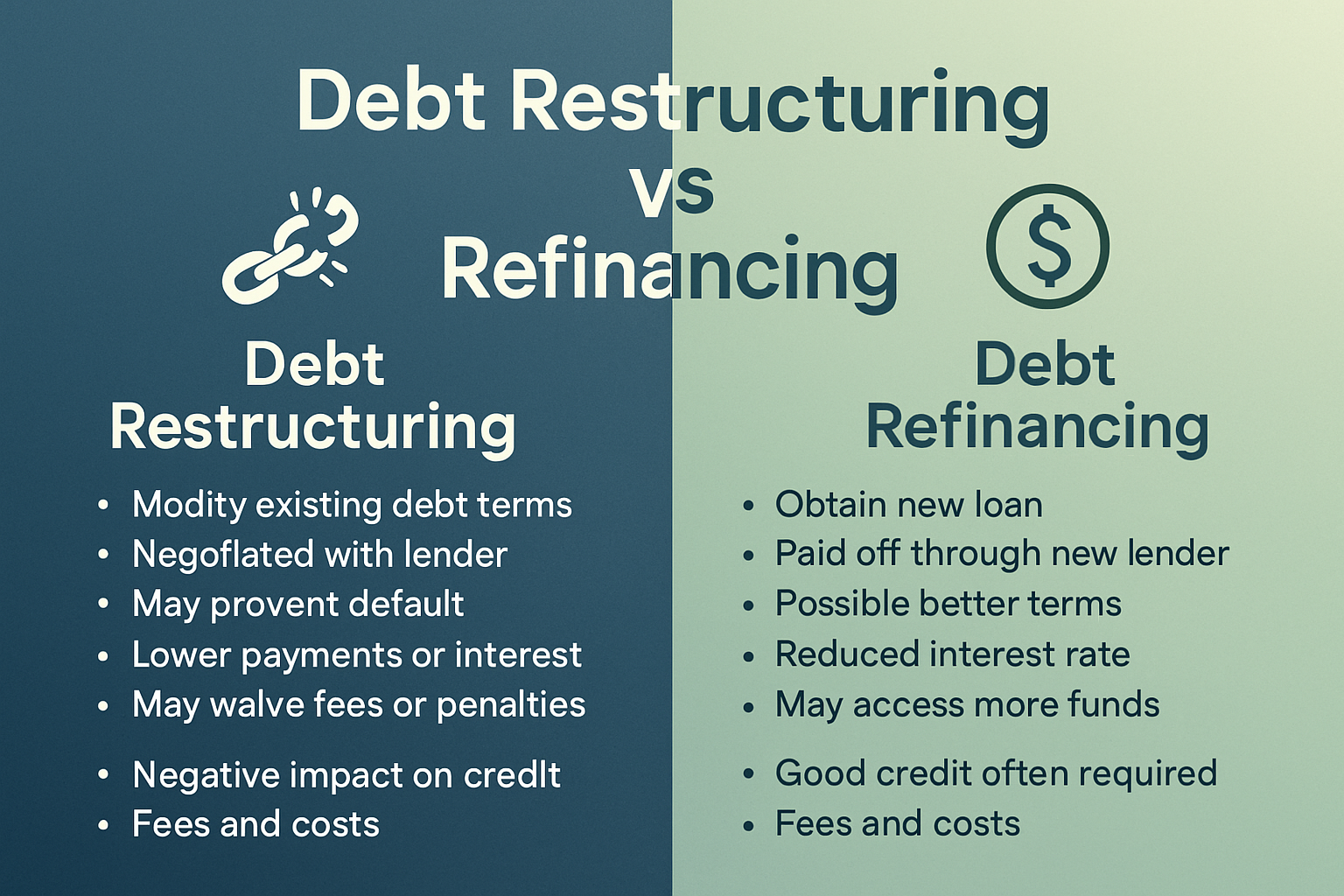
Debt Restructuring vs Refinancing: What’s the Difference?
When you’re dealing with borrowed money, you often have two major options to adjust your debt situation: debt restructuring and debt refinancing. Understanding the difference matters — it can affect your credit score, cost of debt, and long-term financial health. In this article we will explain debt restructuring vs refinancing, so you can make a smart decision.
What is Debt Restructuring?
Debt restructuring is when a borrower and lender negotiate changes to the terms of an existing debt in order to make payments more manageable.
Key characteristics of restructuring
-
The original debt contract remains, but terms are modified (interest rate, payment schedule, tenure) rather than replaced.
-
Typically occurs when the borrower is in financial distress or faces difficulty in meeting obligations.
-
Can include one or more of the following:
-
Extending the repayment period
-
Reducing the interest rate
-
Changing the payment frequency
-
Possibly reducing the principal amount (in more extreme cases)
-
-
It is often seen as a last-resort alternative to default or bankruptcy.
Why might someone restructure debt?
-
Cash flow has diminished and monthly payments are unsustainable.
-
Business or individual expects to recover but needs breathing room.
-
Lender prefers restructuring over the cost and risk of a default.
Pros and cons of restructuring
Pros:
-
Avoids immediate default and potential bankruptcy.
-
Can preserve operations (for businesses) or assets (for individuals) when things are tight.
Cons: -
It may impact your credit score negatively because it signals distress.
-
Sometimes it results in higher total interest cost (if term is extended).
-
Negotiation may be complex and lenders may require proof of hardship.
What is Debt Refinancing?
Debt refinancing means replacing an existing debt with a new debt obligation that has more favorable terms.
Key characteristics of refinancing
-
The old debt is paid off, and a new contract/loan is taken (typically from same or different lender) with better terms.
-
It is usually done by borrowers who are in relatively stable financial position and want to improve their debt terms.
-
Common motivations:
-
Lower interest rate
-
Longer or shorter repayment term depending on strategy
-
Switching from variable rate to fixed rate (or vice versa)
-
Why and when to refinance?
-
Interest rates drop and you can lock in savings.
-
Your credit profile improved and you qualify for better terms.
-
You want to consolidate multiple loans into one or change the loan structure.
Pros and cons of refinancing
Pros:
-
Potential for lower monthly payments and/or lower total interest cost.
-
Opportunity to improve credit profile by closing old debt and replacing with new
Cons:
-
There are often fees, closing costs, or pre-payment penalties on the old loan.
-
Extending the term might reduce the monthly payment but could increase the total interest paid over life of the loan. Wall Street Prep
Restructuring vs Refinancing: Side-by-side Comparison
| Feature | Debt Restructuring | Debt Refinancing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manage financial distress, avoid default | Take advantage of better loan terms |
| Contract change | Modify existing contract | Replace old debt with new contract |
| Borrower’s financial condition | Often weak or unstable | Better financial standing |
| Credit impact | More likely negative or neutral | Potentially positive if executed well |
| Typical changes | Extended term, reduced rate, altered payment | New loan, improved rate/term, consolidation |
| Eligibility | Lender must agree; proof of hardship | Borrower must qualify for new loan |
| Cost implications | May cost more over long-term due to extended term | May save money but watch fees and penalties |
Key Questions and Answers About Debt Restructuring vs Refinancing
When should I consider debt restructuring?
If you are struggling to meet your current debt payments or facing possible default, restructuring may be viable. It gives you breathing room by modifying terms. For example, you might extend the loan term or ask for interest rate concessions.
When should I consider debt refinancing?
If your financial situation is stable and you find a new loan with better interest rates, improved terms or want to consolidate, refinancing could allow you to reduce cost or simplify your debt.
How does each affect my credit score?
Restructuring signals to lenders that you needed relief. This can impact your creditworthiness.
Refinancing, if done well, can improve your credit profile because you’re replacing debt under better terms and remaining current on payments.
What kinds of loans can these apply to?
Both restructuring and refinancing apply to a wide variety of debt types: personal loans, mortgages, business loans, corporate debt, etc.
How to Choose Between Restructuring vs Refinancing
Here’s a quick 6-step decision guide:
-
Review your current debt obligations and monthly cash flow.
-
Are you unable to make payments without trouble? → consider restructuring.
-
Are you able to pay but want better terms? → consider refinancing.
-
Compare costs: new interest rate, fees, term changes, penalties.
-
Talk to your lender about both options and get quotes.
-
Choose the path that yields the lowest risk and cost over the long term.
Case-Studies and Real-World Examples
Example 1: Company in distress – Debt Restructuring
A firm under financial stress unable to meet its payment obligations negotiates with creditors to extend loan maturities and reduce interest rates. This restructuring allows the company to stay afloat and avoid bankruptcy.
Example 2: Homeowner with good standing – Debt Refinancing
A homeowner with a good credit history notices mortgage rates have dropped. They refinance their mortgage to a lower rate, reducing monthly payments or shortening the loan term. This is refinancing in action.
Strategic Considerations for Business & Individual Borrowers
For individuals
-
Make sure you understand fees involved in refinancing — closing costs, pre-payment penalties.
-
If restructuring, check how your lender reports the change and how it may impact your credit.
-
Don’t use refinancing simply to borrow more money without a repayment plan.
For businesses
-
Restructuring may involve renegotiating with multiple creditors, altering covenants, possibly converting debt to equity.
-
Refinancing may be leveraged when market interest rates fall or the business credit profile improves.
-
Always compare the net cost of the new debt vs the existing one including all fees and hidden costs.
Risks & Pitfalls to Watch
-
Hidden fees: Closing costs or prepayment penalties may eat up the savings of refinancing.
-
Term extension trap: While lower payments look attractive, extending a loan term may result in larger total interest.
-
Restructuring stigma: For businesses especially, restructuring signals distress and might hurt investor confidence.
-
Lender refusal: Not all lenders will agree to restructuring unless they believe you’ll repay under the new terms.
-
Timing risk: Refinancing when rates are high or your credit is weak may result in worse terms.
Checklist: Is Restructuring or Refinancing Right for You?
-
✅ Do you have trouble keeping up with current payments? → Restructure.
-
✅ Are you current on payments and want to optimize cost? → Refinance.
-
✅ Are you aware of all fees, costs and long-term impacts?
-
✅ Have you compared multiple lenders and options?
-
✅ Have you estimated the total cost over the life of the loan (not just monthly payment)?
-
✅ Do you have a repayment plan and realistic projection of your future cash flow?
Summary & Key Takeaways
In short: debt restructuring vs refinancing offer different solutions to different problems. Restructuring modifies existing debt for borrowers in distress. Refinancing replaces debt for borrowers seeking better terms and improved financial position. Knowing your financial condition, comparing costs carefully, and choosing the right strategy can make a big impact on your long-term financial health.
Take the first step today — review your current debt, and decide whether restructuring or refinancing is the smarter move for you.